| Outcomes of Nasek / Improving animal welfare / Health and fertility / Diseases / Claw diseases | Wednesday 11.2.2009 |
|
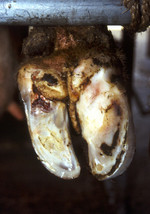
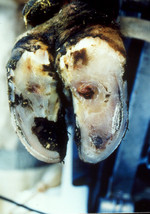
Claw diseases Claw problems are consequences from a bad floor (see also "Floor and walking areas") Problems with claws lead to passive cows, which can cause problems with nutriton of cows, since they cannot walk to a feeding ally or to water as often as healthy cows. And a bad condition and nutrition can cause problems with the fertility,too. Thats why it is important to try to avoid these problem as much as possible . Lameness is almost always a painful condition, and therefore a major animal welfare issue, too. Today lameness is at an unacceptably high level.
The factors that predispose to lameness in dairy cows may be considered under the following headings: • conformation • nutrition/ environment Conformation The most striking feature of foot lameness in dairy cows is that approximately 75% of cases occur in outer claws of a hind feet. This is attributed to aconformation of a cow. The distention of a huge udder splays the back feet out. Nutrition/ Environment
So the following things lead to an increase in claw problems: • Poor farmer's awareness of the causes of lameness and of prevention and treatment
Back to "Diseases" Page updated 23.5.2006 |
|